There are two words you never want to hear in the healthcare industry. Data breach.
It’s a scenario no practice or provider wants to face: patient records exposed, HIPAA compliance at risk, and your reputation hanging in the balance.
Unfortunately, healthcare data security threats are very real and very expensive to deal with. In fact, over 116 million individuals were affected by healthcare data breaches in 2023, costing an industry-wide average of $10.93 million per incident. And it’s not just hospital systems under attack—outpatient practices and specialty providers are among bad actors’ prime targets.
So, what can you do to protect your vulnerable patient data? I recommend employing these four data security tips to minimize vulnerabilities and protect your patients’ sensitive information.
1. Double Down on the “Simple” Stuff
While cutting-edge technologies and complex threat intelligence have value, the key to rock-solid cybersecurity is doubling down on the “simple” stuff. It’s often the fundamentals that act as the first line of defense.
Phishing and Other Common Risks
One of those fundamentals is guarding your practice against phishing. Fake invoices, urgent messages—these are just a few lures in the phisher’s arsenal. And they work. Don’t let your guard down just because you know your way around a computer. As technology and AI advances, so do phishing scams. Phishing is still effective, and that’s why they still do it.
But phishing’s not the only wolf in sheep’s clothing. Third-party access, tech misconfigurations, insecure data transfers, as well as poor data management also pose serious threats.
🔎 Phishing
A technique for attempting to acquire sensitive data, such as bank account numbers, through a fraudulent solicitation in email or on a web site, in which the perpetrator masquerades as a legitimate business or reputable person.
Training Your Staff in Privacy and Security Best Practices
What’s the most simple yet powerful solution to avoiding these risks? Training. Educate your team to spot threats, never click on suspicious links, and double-check every sender. Keep sensitive data under lock and key with passwords that are hard to crack and multi-factor authentication.
Your compliance officer or strategist should keep up to date with best practices and share them with your teams. For example, until recently, it was recommended to update user passwords regularly. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) guidelines have changed: NIST now recommends that businesses enforce password expiration and password resets only when a known compromise has occurred, or every 365 days. The shift to longer password life is intended to encourage users to generate longer and more secure passwords.
2. Stay on Top of System Updates
I get it, system updates are a pain. They can disrupt workflows and require patience, but ignoring updates is like leaving your front door wide open. Hackers exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software, so keeping your systems patched is crucial.
The Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) recommends:
Automating updates whenever possible.
Using trusted vendor sites.
Prioritizing critical updates.
Avoiding untrusted networks during updates.
Clarifying manual vs. automatic options with your IT team.
Adding in extra layers of encryption to secure your platforms.
A single unpatched vulnerability is the open door hackers need to compromise patient data. But, don’t worry. Most updates are quick and painless, with the security benefits far outweighing the inconvenience. I know it’s a pain and you might need to reboot or restart everything—but this is crucial maintenance, because it’ll keep you safe.
3. Know Your Risks
Ignorance is bliss, right? Wrong.
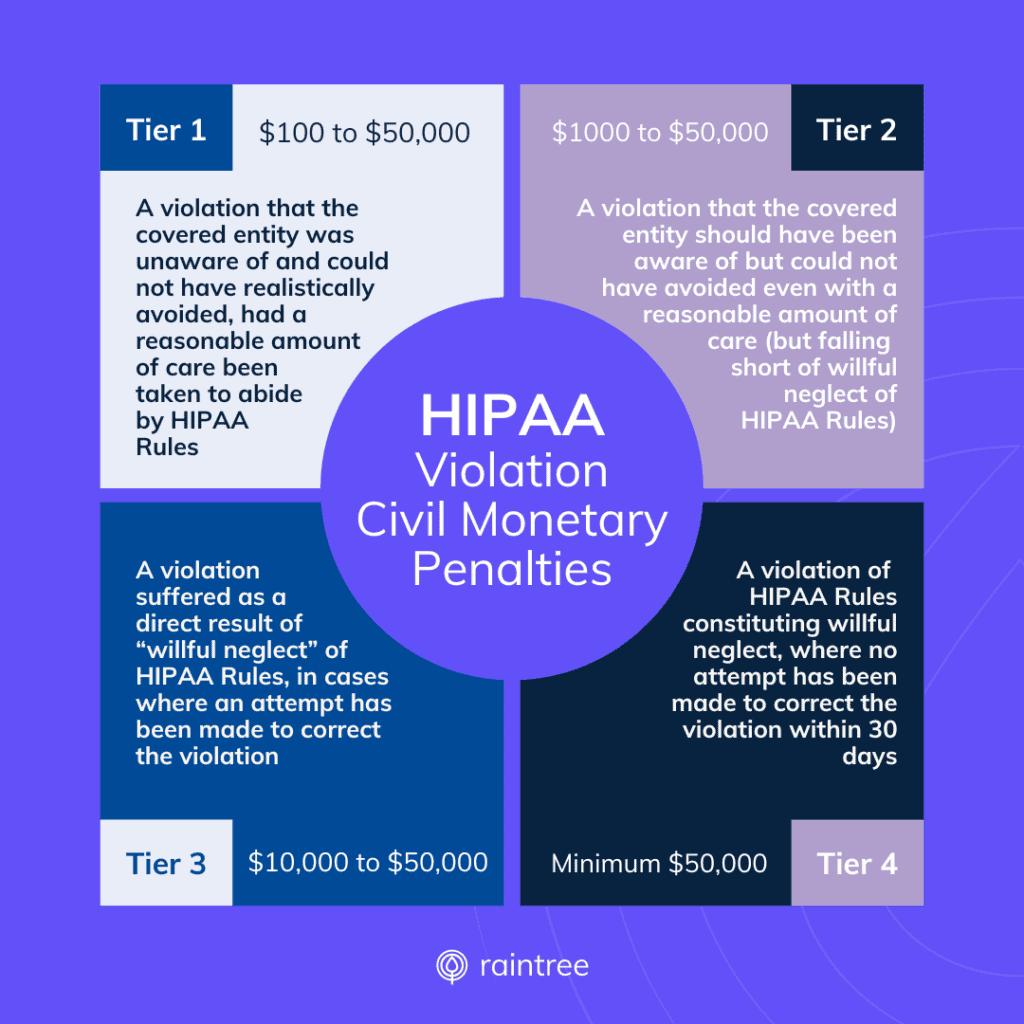
When it comes to data security, being proactive is key—especially in healthcare, where electronic health records containing protected health information (PHI) make prime targets, and violating the HIPAA Privacy Rule can have major consequences.
So don’t just hope for the best—prepare for the worst. Here are some tips for securing private health information, proactively:
- Test your safeguards by simulating phishing attacks or hiring security consultants to discover vulnerabilities. The results of these tests can help you identify where you excel… and where your teams need more security training.
- Conduct regular HIPAA Security Risk Assessments (SRA) to identify specific threats to your patients’ PHI. Additionally, attesting to the completion of your SRA is a requirement of some MIPS reporting programs.
- Continually assess the security of your health IT solutions. Scrutinize vendor security and your Business Associate Agreements (BAAs). Completing the SAFER Guides can help you take a close look at your health IT risks.
- Stay informed by seeking out trusted resources like the HIPAA Journal.
Defense is the best offense against data loss; actively address weak spots to safeguard patient data, your peace of mind, and your business.
4. Create a Culture of Security
Data security in outpatient practices isn’t just a tech issue, it’s a cultural one. Even with sophisticated technological safeguards, human error can be the biggest threat. In my experience, the #1 risk of a data breach is people clicking on a bad link in an email. Or someone calling into a help desk, trying to get information they shouldn’t have. You might not guess it, but social interactions can contain the most risk of compromising data.
In short: You’ve got to make security a priority and a habit. I recommend security awareness training at least once a year, for everyone. In the end, the benefit of implementing best practices far outweighs the financial and reputational cost of a data breach.
Common Misconceptions About Healthcare Data Security
Misconception: Safeguarding your practice is a one-and-done deal.
With the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare, the landscape of health data management is evolving. Familiarize yourself with the most up-to-date regulations, ensuring your AI tools comply with data protection requirements. A strong cybersecurity posture means continuously testing and updating your protocols as cybersecurity tactics progress.
Misconception: Cybersecurity falls solely on IT’s shoulders.
While your IT team should do their part, it takes more than just IT to protect patient data. Any staff that touches or has access to patient information is responsible for protecting PHI. As unauthorized access to patient records storage or views of computer screens can land information in the wrong hands, physical security can pose risks as well.
Misconception: Implementing security measures complicates operations.
Instead, it safeguards data, staff, and patients, bringing peace of mind to everyone. Any organization affected by a breach would tell you, that’s a much bigger headache than staying up-to-date.
Safeguarding Your Practice: The Bottom Line
Data security might not be the most glamorous aspect of running a practice, but it’s vital for protecting your patients, reputation, and business.
Proactively implementing these tips—prioritize the seemingly simple, maintain system updates, understand risks, foster a culture of security—is a strong framework that can reduce the risk of data breaches at your practice.
Here at Raintree Systems, we help physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech-language pathology and multi-disciplinary practices grow and succeed with scalable and robust software solutions. Raintree offers the only ONC-certified EHR system designed specifically for rehab therapy. Want to learn more? Schedule a demo and learn why high-growth PT, OT, SLP, and multi-disciplinary practices choose Raintree.

Don Silva Sr. is Raintree Systems’ Chief Information Security Officer and VP System Ops & Infrastructure. As a senior leader with over 20 years experience leading Global Technology Teams across a variety of industries, he has helped companies grow, mature and align Security & Engineering Teams with business goals. Read Don’s full bio >
Frequently Asked Questions
How can electronic health records improve healthcare organization’s data security?
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) centralize patient data in a secure, digital format. With correct implementation, this can significantly enhance data privacy. EHR systems typically offer advanced security measures such as data encryption, regular backups, and access control, which help in securing private health data.
What measures can healthcare businesses take to prevent a data breach?
To protect healthcare data, healthcare businesses can adopt best practices like conducting regular security audits, reinforcing password security, implementing data encryption, securing mobile devices, regularly having security training for staff and establishing a data backup and recovery system.
How can securing private health data improve patient care?
Patient care relies on trust between providers and the people they're treating, which means privacy is a basic expectation and responsibility. Not to mention: Data breaches can severely impact a practice's reputation.
What is the role of HIPAA in protecting healthcare data in my practice?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets regulations for protecting sensitive patient data. Any healthcare provider that deals with protected health information (PHI) must ensure all necessary security measures are in place and followed. This includes implementing necessary physical and electronic security measures, ensuring HIPAA security training for staff, and reinforcing practices to protect healthcare data.
How does the HIPAA Privacy Rule relate to a healthcare organization’s data security?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule requires healthcare organizations to protect patient data and uphold patient privacy rights. It mandates the use of safeguards to protect PHI and sets limits and conditions on the use and disclosure of such information without patient authorization. It complements the HIPAA security rules, which specifically focus on electronic data security.
Do HIPAA rules dictate specific technologies or software for securing patient data?
While HIPAA security rules require healthcare providers to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and security of PHI, they don't endorse any specific technologies or software. However, they do require certain safeguards, both physical and digital, which often include the use of data encryption, authentication protocols, and secure networks to protect healthcare data.